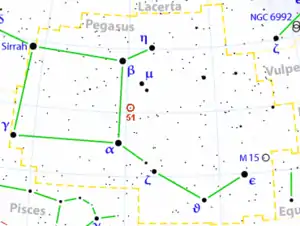
51 Pegasi
51 Pegasi (kısaltma 51 Peg) veya Helvetios, Pegasus takımyıldızında 50.9 ıy[1] uzaklıkta yer alan Güneş benzeri bir yıldızdır. 51 Pegasi, üzerinde bir Güneş dışı gezegen (51 Pegasi b) keşfedilmiş ilk anakol yıldızıdır.[9]
 | ||
| Gözlem verisi Dönem J2000.0 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Takımyıldız | Pegasus | |
| Bahar açısı | (α) | 22s 57d 27.98004sn[1] |
| Yükselim | (δ) | +20° 46′ 07.7912″[1] |
| Görünür parlaklık | (V) | 5.49[2] |
| Sınıflandırma | ||
| Tayfsal sınıf | G5V[3] | |
| R-I Renk ölçeği | 0.32 | |
| V-R Renk ölçeği | 0.37 | |
| J-H Renk ölçeği | +0.67[4] | |
| J-K Renk ölçeği | +0.20[4] | |
| Gökölçümsel nitelikleri | ||
| Dikey hız | (Rv) | −33.7 km/sn |
| Iraklık açısı | (π) | 64.07[1] mys |
| Uzaklık | 50.9 ± 0.3 Iy (15.61 ± 0.09 pc) | |
| mutlak parlaklık | (V) | 4.51 |
| Özdevinim nitelikleri | ||
| Bahar açısı payı | (μ) | 207.25 ± 0.31[1] mys/y |
| Yükselim payı | (μ) | 60.34 ± 0.30[1] mys/y |
| Fiziksel özellikler | ||
| Kütle | (m) | 1.11[3] M⊙ |
| Yarıçap | (r) | 1.237 ± 0.047[2] R⊙ |
| Aydınlatma gücü | 1.30 L⊙ | |
| Yüzey kütle çekimi | (log g) | 4.33[5] cgs |
| Etkin sıcaklık | 5571 ± 102[2] K | |
| Metallik | [Fe/H] | 0.20[5] |
| Dönüş | 21.9 ± 0.4 gün[6] | |
| Tahmini yaş | 6.1–8.1[7] y | |
| Katalog belirtmeleri | ||
| Helvetios, 51 Peg, GJ 882, HR 8729, BD +19°5036, HD 217014, LTT 16750, GCTP 5568.00, SAO 90896, HIP 113357.[8] | ||
Kaynakça
- van Leeuwen, F. (Kasım 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2). ss. 653-664. arXiv:0708.1752 $2. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- van Belle, Gerard T.; von Braun, Kaspar (2009). "Directly Determined Linear Radii and Effective Temperatures of Exoplanet Host Stars". The Astrophysical Journal (abstract). 694 (2). ss. 1085-1098. arXiv:0901.1206 $2. Bibcode:2009ApJ...694.1085V. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/694/2/1085.
- Poppenhäger, K.; Robrade, J.; Schmitt, J. H. M. M.; Hall, J. C. (Aralık 2009), "51 Pegasi – a planet-bearing Maunder minimum candidate", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 508 (3), ss. 1417-1421, arXiv:0911.4862 $2, Bibcode:2009A&A...508.1417P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912945
- Johnson, H. L.; Iriarte, B.; Mitchell, R. I.; Wisniewskj, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. 4 (99). Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- Frasca, A.; Covino, E.; Spezzi, L.; Alcalá, J. M.; Marilli, E.; Fżrész, G.; Gandolfi, D. (Aralık 2009). "REM near-IR and optical photometric monitoring of pre-main sequence stars in Orion. Rotation periods and starspot parameters". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 508 (3). ss. 1313-1330. Bibcode:2009A&A...508.1313F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913327.
- Simpson, E. K.; Baliunas, S. L.; Henry, G. W.; Watson, C. A. (Kasım 2010), "Rotation periods of exoplanet host stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 408 (3), ss. 1666-1679, arXiv:1006.4121 $2, Bibcode:2010MNRAS.408.1666S, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17230.x [as "HD 217014"]
- Eric E., Mamajek; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (Aralık 2008). "Improved Age Estimation for Solar-Type Dwarfs Using Activity-Rotation Diagnostics". The Astrophysical Journal. 687 (2). ss. 1264-1293. arXiv:0807.1686 $2. Bibcode:2008ApJ...687.1264M. doi:10.1086/591785.
- "51 Peg – Star suspected of Variability". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. 28 Nisan 2019 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 11 Nisan 2016.
- Mayor, Michael; Queloz, Didier (1995). "A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star". Nature. 378 (6555). ss. 355-359. Bibcode:1995Natur.378..355M. doi:10.1038/378355a0.
Dış bağlantılar
| Wikimedia Commons'ta 51 Pegasi ile ilgili ortam dosyaları bulunmaktadır. |
- Jean Schneider (2011). "Notes for star 51 Peg". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. 3 Haziran 2012 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 11 Nisan 2016.
- 51 Pegasi25 Temmuz 2008 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi. at SolStation.com.
- nStars database entry
- David Darling's encyclopedia 3 Mart 2016 tarihinde Wayback Machine sitesinde arşivlendi.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.